Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MariaDB group by clause to group data.
Introduction to MariaDB group by clause
The group by clause groups rows of a result into groups. The following illustrates the syntax of the group by clause:
select
select_list
from
table_name
group by
column1, column2,...;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The group by is often used with aggregate functions including count(), min(), max(), sum(), and avg() to find properties of groups such as the number of elements (count), the total of values (sum), the maximum element (max), the minimum element (min), and the average of elements (avg).
The following shows the syntax of the group by clause used with an aggregate function:
select
column1,
aggregate_function(column2)
from
table_name
group by
column1;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In this syntax, the group by clause groups rows into groups and the aggregate function is applied to each group to return the summary row.
MariaDB group by clause examples
We’ll use the countries and regions tables from the nation sample database for the demonstration.
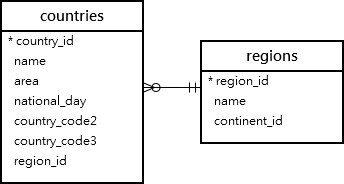
A) Using the MariaDB group by clause with the count() function example
The following statement uses the group by clause with the count() function to get the number of countries in each region:
select
region_id,
count(country_id)
from
countries
group by
region_id
order by
region_id;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)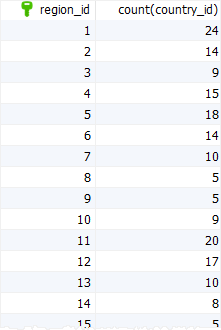
In this example:
- First, the
group byclause divides the countries by regions. - Then, the
count()function is applied to each region to return the number of countries.
To make the output more meaningful, you can join the countries table with the regions table:
select
regions.name,
count(country_id) country_count
from
countries
inner join regions using (region_id)
group by
regions.name
order by
regions.name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)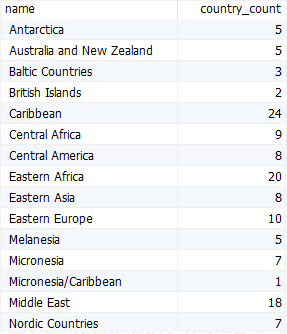
B) Using the MariaDB group by clause with the sum() function
The following example uses the group by clause with the sum() function to calculate the total area of countries in each region:
select
regions.name region,
sum(area) region_area
from
countries
inner join regions
using (region_id)
group by
regions.name
order by
region_area desc;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)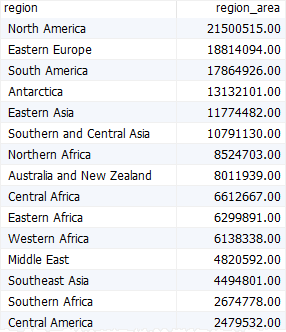
C) Using the MariaDB group by clause with themin() and max() functions
The following example uses the group by clause with the min() and max() functions to find the minimum and maximum areas of countries in each region:
select
regions.name region,
min(area) smallest_country_area,
max(area) largest_country_area
from countries
inner join regions using (region_id)
group by
regions.name
order by
regions.name;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)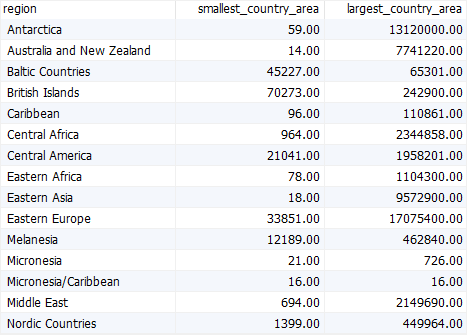
D) Using the MariaDB group by clause with the avg() function
The following example uses the group by clause with the avg() function to calculate the average area of countries in each region:
select
regions.name region,
avg(area) avg_area
from
countries
inner join regions
using (region_id)
group by
regions.name
order by
avg_area desc;
Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)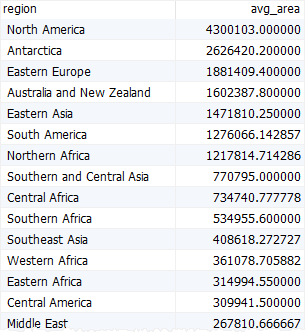
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the MariaDB group by clause to group data.